Installing Observer
This section will guide you through the installation process for AnyShake Observer.
Supported Platforms
AnyShake Observer runs on a wide range of platforms. Some architectures also support Docker images (highlighted in bold):
- Android (arm64)
- macOS (amd64 / arm64)
- FreeBSD (x86 / amd64 / arm / arm64)
- Windows 7 and later (x86 / amd64 / arm / arm64)
- Linux (x86 / amd64 / arm / arm64 / ppc64le / riscv64 / s390x / mips / mips64 / mips64le / mipsle / loong64)
In fact, AnyShake Observer can even run on a Raspberry Pi 1 Model B+ (overclocked to 950 MHz, with 100 MB of swap) with all core services enabled!
Although AnyShake Observer has very modest hardware requirements, we recommend using a system with at least 1 GB of RAM and a dual-core CPU for a smoother experience.
Installation Options
Depending on your platform and preferences, there are several ways to install AnyShake Observer. This section covers the most common and recommended method.
Pre-Built Packages
This is the recommended installation method for most users. Pre-built packages are stable, easy to install, and require minimal configuration.
Download the Binary
Pre-built binaries are available on the GitHub Releases page of the AnyShake Observer repository:
Check out github.com/anyshake/observer/releases
Each release includes assets named like:
windows_amd64.zip– Windows 64-bitlinux_arm32_v7a.zip– Linux ARM 32-bitmacos_arm64.zip– macOS Apple Silicon
All pre-built packages are provided in .zip format. Download the one that matches your system, then unzip it to any directory.
You will also find .dgst files such as linux_amd64.zip.dgst – these contain MD5, SHA1, SHA2-256, and SHA2-512 digests for verifying file integrity.
Determine Your System Architecture
To find the correct binary, determine your system’s architecture:
For Windows users:
Open cmd and type:
> echo %PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE%
- If you see
x86, you’re on 32-bit Windows, use a package with_386suffix. - If you see
AMD64, you’re on 64-bit Windows, use a package with_amd64suffix. - For Windows 7 users, use the package with
windows7_prefix.
For Linux users:
Use this command:
$ uname -m
- If it returns
x86_64, use the_amd64package. - If it returns
i686, use the_386package. - For ARM devices like Raspberry Pi, it may return
armv7l,aarch64, etc. Remember to choose the appropriatelinux_arm*package accordingly.
Verify the Downloaded File
Each .zip file has a corresponding .dgst digest file. You can verify the integrity of the downloaded binary using:
$ cat linux_amd64.zip.dgst
MD5 = dd3a79d4baf00bcf09ad3b325d5d516b
...
$ echo "dd3a79d4baf00bcf09ad3b325d5d516b linux_amd64.zip" | md5sum -c
linux_amd64.zip: OK
Replace linux_amd64.zip and the hash with the appropriate filenames and values for your system.
Install the Binary
After extracting the ZIP package, you’ll find the following files:
observer.exe– Windows executableobserver– Linux/macOS executableconfig.json– Default configuration fileobserver.service– Linux systemd service file (optional)
The default config.json may not be suitable for your system, so you need to edit it or generate a new one to override the default values before copying. We recommend using the AnyShake Prisma to generate a new configuration, see Configuration Tool to learn more.
For Windows users:
- Create a directory, for example,
C:\Program Files\AnyShake Observer.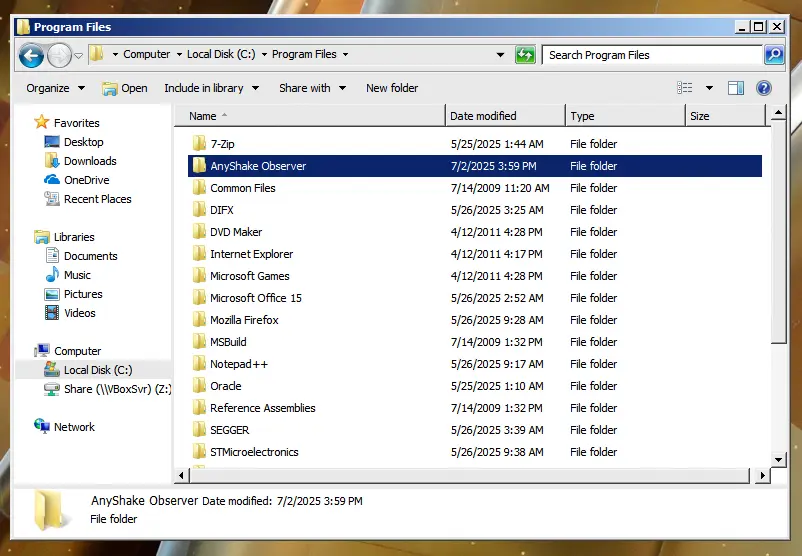
- Place
observer.exeandconfig.jsonin the newly created directory.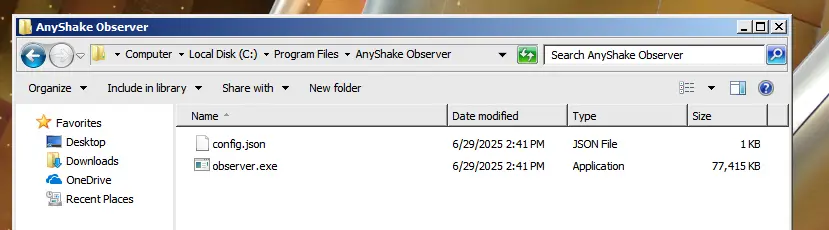
For Linux users:
- Add your user to the
dialoutgroup (for serial port access):
$ sudo usermod -a -G dialout $USER
- Create the configuration directory and copy
config.json:
$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/etc/observer
$ sudo cp config.json /usr/local/etc/observer/
- Copy the binary to a system path:
$ sudo cp observer /usr/local/bin/
- To verify the installation:
$ which observer
/usr/local/bin/observer
Docker Image
If you prefer containers, an official Docker image is available.
The Docker installation method is not recommended for Windows users, as it is difficult to map serial devices properly.
Pull the Image
$ docker pull ghcr.io/anyshake/observer:latest
Run the Container
Mount the config file and, if applicable, the serial port:
$ docker run -d \
--name observer \
--network host \
--restart always \
--device /dev/ttyUSB0:/dev/ttyUSB0 \
--volume /path/to/config.json:/config.json \
ghcr.io/anyshake/observer:latest \
--config /config.json
- Replace
/path/to/config.jsonwith the actual path on your host - Replace
/dev/ttyUSB0with your actual serial port if applicable
If you don’t use a hardware serial connection, the --device flag is not needed.